OSTEOPATHIE
Filosofie van
de osteopathie
De filosofie van osteopathie
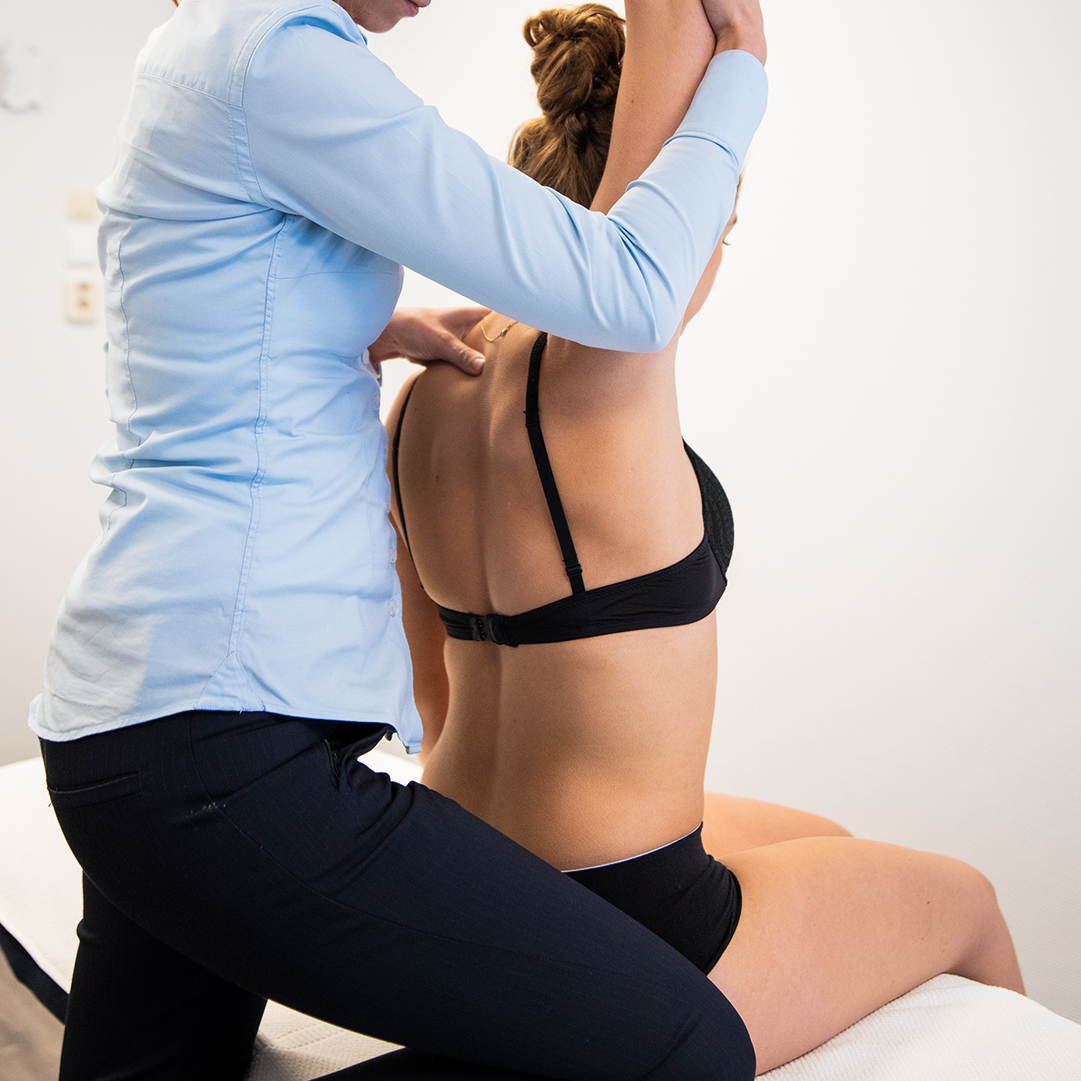
Sinds haar ontstaan in 1874, heeft osteopathie zich ontwikkeld tot een volwaardige medische wetenschap. Daarbij hebben de vier basisprincipes die ten grondslag liggen aan osteopathie een belangrijke rol gespeeld:
1. Leven is bewegen en bewegen is leven
“Life is motion”, de woorden van de grondlegger van de osteopathie Dr. A.T. Still. Alles in ons lichaam moet bewegen om te kunnen leven. Dit principe geldt voor alle grote, maar ook voor alle kleine bewegingen binnen een gewricht, orgaan of ons zenuwstelsel.
2. Het lichaam functioneert als een eenheid
Klachten die zich uiten op een bepaalde plek in uw lichaam, kunnen wijzen op bewegingsverlies van een ander deel van uw lichaam. Het is daarom belangrijk om verder te kijken dan alleen de klacht.
3. Het lichaam probeert altijd zo optimaal mogelijk te functioneren
Minder beweging ergens in uw lichaam hoeft niet direct tot klachten te leiden. Uw lichaam zal de tekortkoming zoveel mogelijk compenseren, waarbij het kan zijn dat u gewoon normaal blijft functioneren. Omdat u vanaf nu extra werk verricht om te compenseren voor een tekortkoming, verbruikt u waarschijnlijk wel meer energie dan normaal.
4. Structuur en functie van het lichaam zijn wederkerig aan elkaar
Structuur en functie zijn onlosmakelijk aan elkaar verbonden en als zodanig beïnvloeden zij elkaar. Voor het optimaal functioneren van het menselijk lichaam, is het noodzakelijk dat de afzonderlijke delen van het lichaam hun functie op natuurlijke wijze kunnen uitoefenen.
Hoewel de omschrijving van het beroep osteopaat per land kan verschillen, is er een internationaal consensus over de huidige definitie van het vakgebied of domein.
European Federation of Osteopaths (EFO) en Forum for Osteopathic Regulation Europe (FORE) hebben in 2012 het document: The scope of Osteopathic Practice in Europe opgesteld, waarin het vak Osteopathie in Europa gedefinieerd wordt (EFO & FORE ,2012). De verklaringsmodellen zijn opgesteld door de Educational Council on Osteopathic Principles (ECOP). Deze organisatie beschrijft hoe de effecten van manuele interventies kunnen worden verklaard middels 5 theoretische modellen. De volgende tekst dient hiervoor als basis:
The practice of osteopathy uses current scientific knowledge to apply the principles of osteopathy to patient care. Scientific plausibility and evidence-based outcomes have a high priority in patient treatment and case management.
Osteopathy provides a broad range of approaches to the maintenance of health and the management of the disease. It embraces the concept of the unity of the individual’s structure (anatomy) and function (physiology); as such osteopathy is a patient-centered system of health care, rather than disease-centered.
An essential component of osteopathy is its great attention to body mechanics and its manual methods in diagnosis and therapy. Osteopathy was developed as a means to facilitate normal self-regulation/ self-healing mechanisms in the body by addressing areas of tissue strain, stress, or dysfunction which may impede normal neural, vascular, and biochemical mechanisms.
The practical application of the concepts and principles are described by several models of structure-function relationships that osteopathic clinicians use to influence the gathering of diagnostic information and the interpretation of the significance of neuro-musculoskeletal findings in the overall health of the patient.
The following 5 models of structure-function guide the osteopathic clinician’s diagnosis and treatment of the patient. The models describe the effects of postural and biomechanical factors on the patient’s ability to compensate for stresses or illness; the influence of the nervous system in maintaining proper cell and tissue function; the role of psychosocial factors in preventing and treating disease; and factors which influence bio-energetic needs such as oxygen and nutrient consumption.
These models are:
- Biomechanical model
- Neurological model
- Respiratory/ Circulatory model
- Bio-psychosocial model
- Bio-energetic model
It is of course for a thorough knowledge of the physiological mechanisms of these models to be taught extensively in an osteopathic curriculum.
Osteopathie in de Verenigde Staten
In de ECOP, dat het document heeft opgesteld, hebben ook afgevaardigden van Amerikaanse osteopathie-universiteiten zitting. De organisatie is een onderdeel van de American Association of Colleges of Osteopathic Medicine (AACOM). Doel van dit expertpanel was om consensus te verkrijgen over het gebruik van de terminologie en modellen in de osteopathie. De hierboven genoemde osteopatische verklaringsmodellen werden voor het eerst in 1981 gepubliceerd en in 2009 voor het laatst herzien. In 2006 erkende de World Health Organisation (WHO) het osteopatisch vijfmodellen concept als een unieke osteopatische bijdrage aan de wereldgezondheidszorg.
World Health Organisation (WHO)
‘Osteopathy is a system of medicinet that emphasizes the theory that the body can make its own remedies, given normal structural relationships, environmental conditions, and nutrition. It differs from allopathy primarily in its greater attention to body mechanics and manipulative methods in diagnosis and therapy (WHO, 2010).





 English
English